When it comes to fueling your body for peak performance as an athlete, the type of diet you follow can play a significant role in your overall fitness and health. In recent years, the debate between vegan and non-vegan diets for athletes has been a hot topic in the fitness community. Each side has its arguments and supporters, but which one is truly the best for athletes? Let’s break down the differences and benefits of each diet to help you make an informed decision.
What is a Vegan Diet?
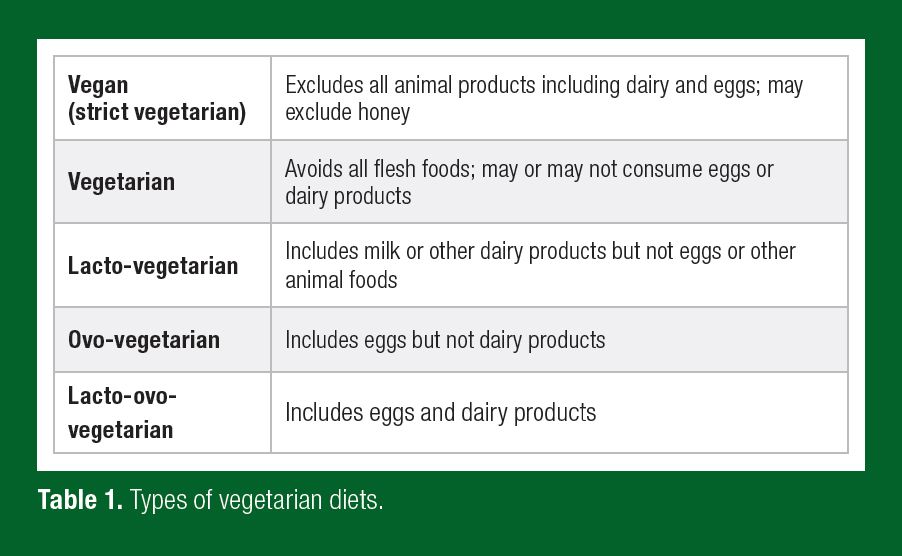
A vegan diet is a plant-based diet that eliminates all animal products, including meat, dairy, eggs, and even honey. Instead, vegans rely on fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds to meet their nutritional needs. Many athletes choose a vegan diet for ethical reasons, environmental concerns, or health benefits.
Benefits of a Vegan Diet for Athletes
Improved Heart Health: A vegan diet is naturally low in saturated fat and cholesterol, which can reduce the risk of heart disease and improve cardiovascular health.
Enhanced Recovery: Plant-based foods are rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties, which can aid in faster recovery after intense workouts.
Weight Management: Many athletes find it easier to maintain a healthy weight on a vegan diet due to its high fiber content and lower calorie density.
Increased Energy: Plant-based foods are rich in complex carbohydrates, which provide a steady source of energy for endurance athletes.
What is a Non-Vegan Diet?
A non-vegan diet includes animal products such as meat, dairy, eggs, and fish. Many athletes follow a non-vegan diet for its high protein content and potential muscle-building benefits. Some athletes also believe that animal products are essential for optimal performance and recovery.
Benefits of a Non-Vegan Diet for Athletes
High Protein Intake: Animal products are a complete source of protein, which is crucial for muscle repair and growth in athletes.
Iron and Vitamin B12: Animal products are rich in iron and vitamin B12, which are essential for energy production and oxygen transport in the body.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Fish and seafood are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties and can improve heart health.
Convenience and Availability: Non-vegan options are widely available and can be convenient for athletes on the go.
Which Diet is Best for Athletes?
Ultimately, the best diet for athletes depends on individual preferences, nutritional needs, and performance goals. Some athletes thrive on a vegan diet and experience improved endurance, faster recovery, and enhanced overall health. Others may find that a non-vegan diet helps them build muscle, increase strength, and maintain energy levels.
It’s essential to work with a registered dietitian or nutritionist to create a personalized meal plan that meets your specific needs as an athlete. They can help you determine the right balance of macronutrients, vitamins, and minerals to support your training and performance goals.
Conclusion
Whether you choose a vegan or non-vegan diet as an athlete, the key is to prioritize nutrient-dense, whole foods that support your performance and recovery. Both diets have their benefits and challenges, so it’s essential to listen to your body and make informed choices based on your individual needs.
Remember, the most important factor in fueling your body as an athlete is to maintain a healthy, balanced diet that provides you with the energy and nutrients you need to excel in your sport. Experiment with different foods and eating styles to find what works best for you and helps you reach your athletic goals.